"What day stack? Twelve points? Sun, moon and security? Li Xing An Chen? " -Qu Yuan’s "Tian Wen"
Is there any margin in the vast starry sky? Is there extraterrestrial life in the vast universe?
Guo Shoujing telescope (LAMOST), Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST) (FAST), high-altitude cosmic ray observatory (LHAASO) and China’s three "sky-watching heavyweights", what cosmic whispers have you heard?
On the stage of "Science and Technology New Year Show" in 2024-"Science Night" at the main station, the speech and dance of "Beauty of Science" were specially presented. In order to present the breathtaking beauty of science in more dimensions, the Social Education Program Center of the General Station plans to launch the extended brand "Science Night" of the General Station-"Beauty of Science". The film is under the professional guidance of China Association for Science and Technology.

With the theme of five natural mysteries, The Beauty of Science (the first season) invited six academicians of China Academy of Sciences: Wang Enge, a physicist and former president of Peking University, Cui Xiangqun, a lichen mycologist, Muming Poo, a neurobiologist and biophysicist, Luo Qingming, a bioimager and president of Hainan University, and Cheng Heping, a cell biologist and biophysicist, to share their understanding of the beauty of science. It presents a pure, extreme and gorgeous visual spectacle by combining ultra-microscopic photography, scientific experiments and field visits. Record the symbiosis of science and art, and sing the symphony of wisdom and sensibility.
As early as the ancient times, the vastness and magnificence of the Milky Way aroused the infinite curiosity of mankind. CCTV-10 will broadcast the third episode of "The Beauty of Science" at 21:20 pm on Sunday (April 27th). Astronomer and Academician Cui Xiangqun of China Academy of Sciences will explain how Guo Shoujing Telescope (LAMOST), Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST) (FAST) and high-altitude cosmic ray observatory (LHAASO) can explore hidden in the starry sky.
Guo Shoujing telescope LAMOST:
The "gene sequencing officer" of cosmic celestial bodies
When the stars light up the night sky, at the top of the mountains in Xinglong County, Hebei Province, "Starcatcher" LAMOST quietly wakes up. Behind the mirror, 16 spectrometers were started synchronously, and 4,000 optical fibers were precisely arrayed, locking 4,000 target celestial bodies one by one, and splitting the light from celestial bodies into spectra with different wavelengths, which were recorded and archived by 32 CCD cameras independently developed by China.

△LAMOST opening moment

△ beautiful starry sky
LAMOST’s mission is not to shoot the beauty of the starry sky, but to decode the truth of the universe hidden in the starlight. The light emitted by each star has a unique spectrum, which is like a gene fragment of a cosmic celestial body and records the unique identity information of each celestial body.
As the largest spectral survey telescope in the world, LAMOST is building a cosmic archive for the stars at the speed of scanning tens of thousands of cosmic objects every night.
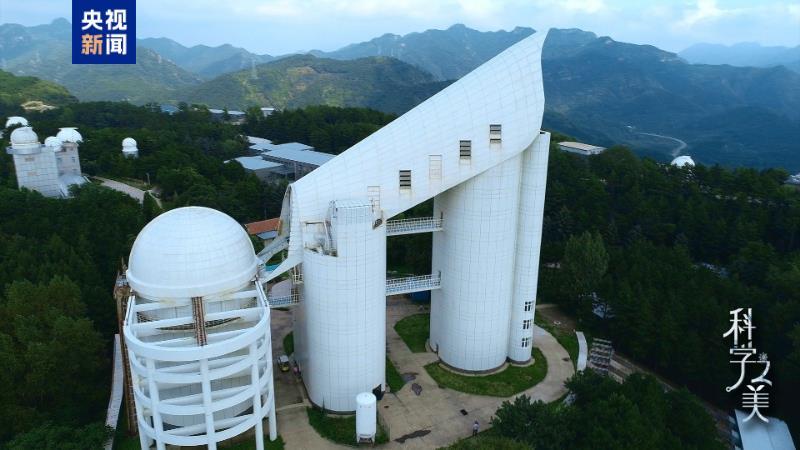

△ Guo Shoujing telescope LAMOST
LAMOST is called "large-sky-area multi-target optical fiber spectrum astronomical telescope", named after Guo Shoujing, an ancient astronomer in China. Since the launch of the sky survey program in September 2012, LAMOST has observed the spectra of more than 25 million cosmic objects. The more we know about the stars in the universe, the more data we can provide for the future exploration of the universe, and let mankind take a step closer to the vast starry sky.
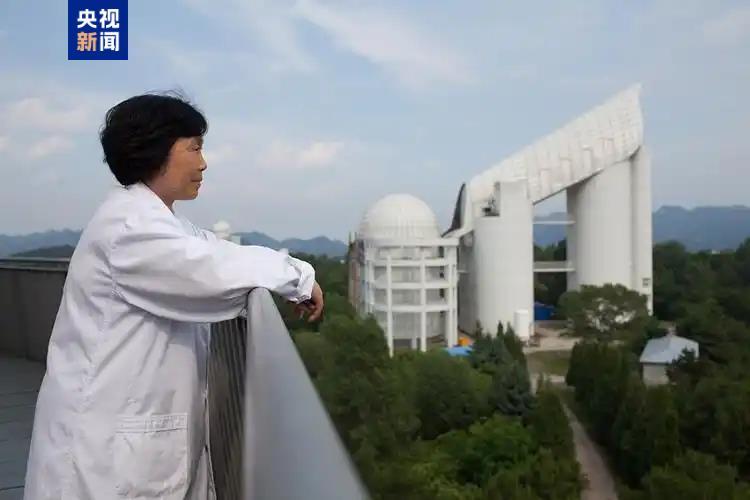

△ Academician of China Academy of Sciences Cui Xiangqun
Cui Xiangqun, an astronomer and academician of China Academy of Sciences, said: "We developed telescopes to observe increasingly dark and distant celestial bodies. We are pursuing a limit, and the universe that human beings realize is getting closer and closer to the truth of nature. "
"Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST)" FAST:
Listen to the "heartbeat" of the universe
In 2021, a series of intermittent radio signals received by Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST) FAST excited many astronomers. These mysterious signals from outer space were repeated 1652 times in 47 days, and some even speculated whether they came from alien life. Scientists have analyzed that these signals come from distant space 3 billion light years away.
Although FAST is called "Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST)", its task is not to look at the stars, but to "listen" to the universe. Just as bats can tell the direction with their own ultrasonic waves, FAST can obtain information about the universe through electromagnetic waves.

△ "Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST)" FAST
The full name of "Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST)" FAST is "500-meter spherical radio telescope". As the largest radio telescope in the world, the detection distance of FAST is almost close to the edge of the universe.
Since its official opening in 2020, FAST has discovered more than 1,000 pulsars. These "lighthouses" in the depths of the universe mark the deep space coordinates for human beings with special pulses and stable rotation frequency. In the future, when the "lighthouse coordinate system" covers a wider interstellar space, it will become the "cosmic GPS" for interstellar travel, guiding the spacecraft through the dark territory of light-year scale.

△ "Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST)" active reflector
Why can FAST "listen" so far? The answer lies in the "big eyes" surrounded by mountains in Guizhou: the super reflective surface of FAST can be stretched from a sphere to a paraboloid; Six 100-meter steel towers lock deep space signals with 10 mm accuracy, and gather weak signals hundreds of millions of light-years away into focus.
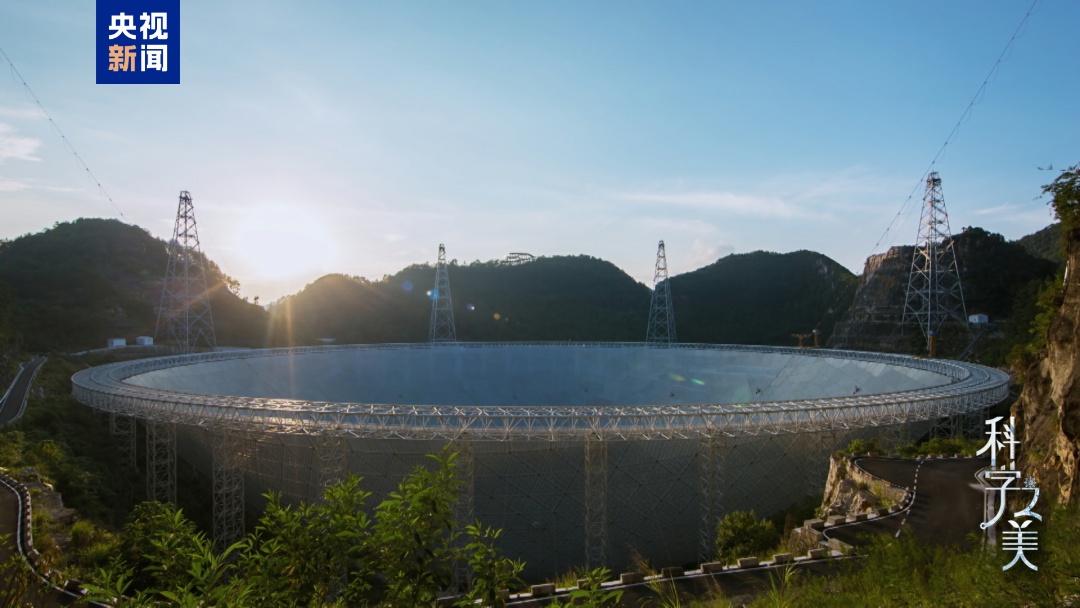

△ "Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST)" FAST
High altitude cosmic ray observatory "lasso" (LHAASO);
The mysterious "cosmic post office" on the plateau

△ "lasso" panorama

△ "Lasso" at night
At 21: 20: 50 on October 9, 2022, more than 60,000 gamma photons were recorded by Lasso, which was the afterglow of a star funeral 2 billion light years away. A giant star with a mass 20 times that of the sun collapsed after running out of nuclear fuel, releasing a "cosmic fireworks" gamma-ray burst lasting several hundred seconds.
On the detector array of Lasso, the moment when "cosmic fireworks" splashed was collected. This is the first time that human beings have completely recorded the "life cycle" of the trillion electron volt gamma ray burst from birth to annihilation. Because such events happen once in a blue moon, the data of Lasso will remain the "best observation record of the universe" in the next hundred years.
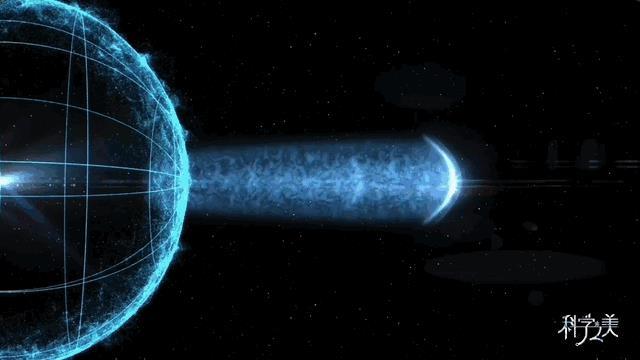
△ Simulation animation of gamma-ray bursts reaching the Earth
"Laso" stands on the 4410-meter plateau in Daocheng, Sichuan. It is not a telescope in the traditional sense, but a "cosmic post office" composed of 5,216 electromagnetic particle detectors, 1,188 Muzi detectors and 18 wide-angle Cherenkov telescopes. Its mission is to intercept cosmic rays in the universe like "time and space stationery".

△ "Lasso" Cherenkov telescope works
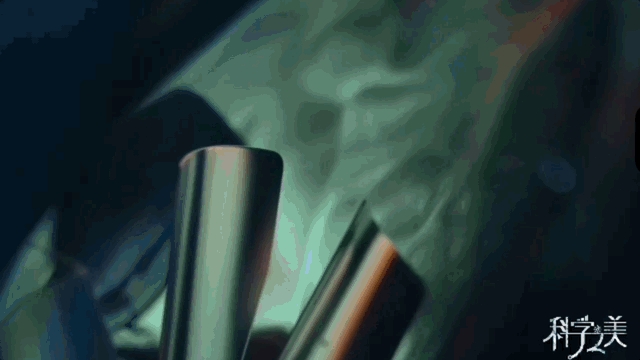
△ "Lasso" water Cherenkov detector array
Cosmic rays are "raindrops" in deep space and "time drift bottles" of distant celestial bodies. They carry the code of celestial evolution and knock on the earth at a speed close to the speed of light.

△ "Cable" electromagnetic particle detector and Muzi detector
LAMOST writes biographies of stars with visible light, FAST listens to whispers in deep space with radio waves, and Lasso traces the history of the universe with gamma rays. Every discovery of these astronomical devices is trying to answer "Where did we come from? Where is the universe finally? "

△ Weather changes above "Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST)"

△ Foreign radio telescope
The scientific and technological progress and influence brought by scientific apparatus can hardly be measured by the current short-term achievements. Every major breakthrough will "inadvertently" bring great shock and impetus to the whole basic discipline and even the process of human civilization.
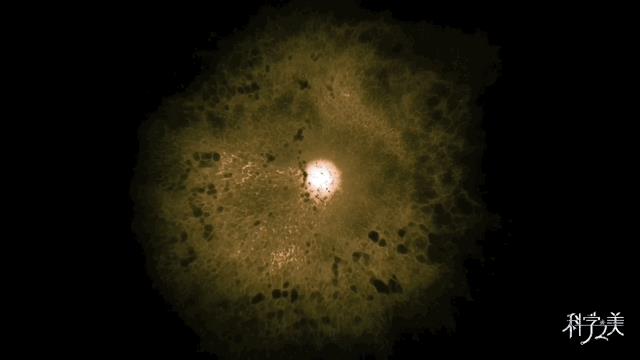
△ Cosmic Nebula Simulation Animation
Academician Cui Xiangqun also talked about the significance of human beings inquiring about the sky and surveying the sky: "When you see the starry sky, everyone will feel that people are very small. Even if you live for 100 years, it is only a moment on the scale of the universe. So we have to do something interesting. This interesting thing makes you feel that you have not lived in vain and contributed to the progress and development of human civilization. "

△ beautiful starry sky
In front of the 13.8 billion-year-old universe, the history of human beings is like a moment, but it is the existence of this moment that allows us to use electromagnetic waves as a pen to write annotations belonging to human beings on the curtain of time and space.
The Beauty of Science, Episode 3, Asking for Heaven
At 21:20 pm on April 27th, 2025.
CCTV-10 science education channel
See China Astronomical scientific apparatus.
On a light-year scale
Measuring the deepest mysteries of the universe
关于作者